Now more than ever digital transformation is profoundly changing manufacturing, processing and production industries all around the world. Recent research conducted by Raoul Sisodia and Daniel Villegas Forero indicates how to transition into Quality 4.0. In our blog, based on their research findings, we zoom in on Quality 4.0 initiatives.
First things first: how can we define Quality 4.0? The concept derived from the fourth industrial revolution, called Industry 4.0. It refers to the digitalisation of total quality management (TQM) and how digital tools can impact technology, process and people.
The ISO 9001:2015 standard provides us with guidelines for the adoption of a quality management system related to TQM. As it proposes seven Quality Management principles that should work under a process approach:
- Customer focus
- Leadership
- Engagement of people
- Process approach
- Improvement
- Evidence-based decision making
- Relationship management
However, how to transition into Quality 4.0 remains abstract and intangible for many companies.
It is important to note that in the context of Industry 4.0, quality should be considered as the discovery of data sources, root causes and insights about products and organisations by augmenting, and improving upon, human intelligence. The changes that comes with digitalisation, automation, big data and cybersecurity must therefore be considered as organisational issues.
Sisodia et al. proposed the following general roadmap for transition to Quality 4.0, which comprehends six sequential phases and is applicable to different organisations.
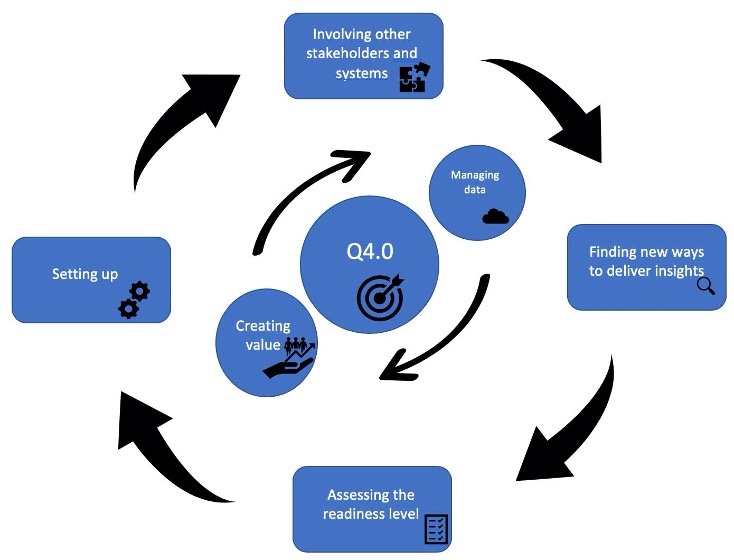
1. Assessing the readiness level
- Assess the industry 4.0 maturity level
- Assess the stability of processes and data flows
- Monitor regulations and standards
2. Setting up
- Align strategy to industry 4.0
- Develop business cases and secure management support
- Anticipate changes
- Manage knowledge
3. Involving stakeholders and systems
- Address changing roles and competences
- Involve suppliers
- Involve customers
- improve the interoperability of systems
4. Finding new ways to deliver insights
5. Creating value: overlaps with all the other phases where value is created in each on of them.
6. Managing data
- Have the adequate infrastructure for administering data and dataflows, bringing the right insights to people in a timely fashion, for doing their work better.
Researchers (Radziwill et al) argue that there are seven tools and technologies that can be used to improve quality and its’ digitalisation:
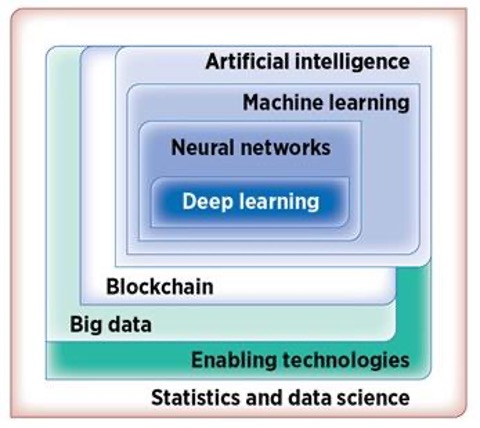
- Statistics and Data Science:
Drive value through predictions, finding patterns and generate viable models and solutions. Identify causal and non causal relationships through data aggregation, data classification, real-time pipelines and dynamic modeling that generates knowledge related to problem-solving
- Enabling technologies:
Always related to the latest developments in connectivity like sensors, mobile devices, networks, Internet of Things (IoT), Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), integrated systems, Virtual Reality and cloud computing. Also related to how to manage documentation.
- Big data:
Related to the infrastructure for managing and analysing large data sets that arrive very fast, in different formats, with high variation in data quality, from different stakeholders, could be easily modified and when there may be restrictions for its use.
- Blockchain:
Permanent monitoring for allowing transactions to happen only if quality objectives are met. Contributes to ensuring data quality, trust and to develop a quality culture.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI):
For making complex decisions like computer vision, chatbots and robotics.
- Machine Learning (ML):
It helps when heuristics are used for decision making and also for forecasting, filtering of information and recommendation systems. Helps a company to do jobs better by finding levers within the processes that can ensure consistency and alignment across the whole organisation. The uncovering of relationships helps build a safety and quality culture.
- Neural Networks and Deep Learning:
Used for forecasting and complex pattern recognition. It incorporates layers with special functions.
Subsequently the role of quality professionals continues to change, as they need to help their organisations make the vital connection between quality excellence and their ability to thrive in disruption, using quality principles to enable transformation and growth. With Quality 4.0 quality professionals all be more capable to answer questions about:
- product robustness
- process excellence
- customer satisfaction
- risks in new product development
- traceability
- transparency
Quality professionals possess the necessary skills to lead digital transformation in organisations, such as;
- systems thinking,
- decision making based on data,
- leadership for organisational learning,
- continuous improvement processes
- the ability to understand the consequences of decisions taken regarding society, environment and ethics.
Furthermore, the role of existing inspection will evolve as well. Since measuring of performed operations will be done by automated equipment built into the machines and production lines, inspectors will have to shift their role. Inspectors will play crucial roles in making decisions related to measuring processes, analyzing collected data, and taking appropriate preventive measures to improve existing processes.
Quality 4.0 blends new technologies with traditional quality methods to arrive at new optimums performance, operational excellence and innovation.
Are you ready to start the quality transition journey? Contact us today and find out more about how Pinnaql can support you.
